How much battery storage do I need? A Step by Step Guide
Deciding to invest in home energy storage is a major step towards energy independence. But with a growing number of choices, figuring out the right system can feel overwhelming. How much battery storage do I need? Which brands can I trust?
This guide will walk you through everything, helping you understand your needs and compare the best options on the market. We will break down all the factors you need to consider, from your daily electricity habits to your future energy goals. By the end, you’ll have a clear, practical method for determining the perfect battery size for your home.
Step 1: Understand Your Household’s Energy Consumption
Before you can choose a battery, you need to know how much electricity your home actually uses. The most accurate way to find this is by looking at your utility bills. Your supplier provides statements showing your energy use in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Look for your average daily consumption. For most UK homes, this figure is typically between 8 kWh and 10 kWh per day.
If you can’t find a daily average, you can calculate it. Take your monthly or quarterly kWh usage and divide it by the number of days in that period. This number is your starting point—the foundation for all other calculations.
Step 2: Define Your Primary Goal for Battery Storage
Your goal is the most important factor. Investing in a home energy storage system is a significant step, and knowing exactly what you want to achieve with it is key to making the right choice. If you just need to keep the lights on and the fridge cold during a storm, a smaller battery might be enough. If you dream of true energy independence, you’ll need a system large enough to cover your total daily consumption.
Before diving into models and technical specifications, it’s essential to define your primary goal. Are you aiming for greater energy independence, looking to reduce your monthly utility bills, or looking to power your home when power outages occur? By clearly identifying your main objective, you can more easily navigate the options and select a home energy storage system that perfectly aligns with your household’s specific needs.
Maximise Solar Self-Consumption
This is the most common goal. You want to store excess solar energy generated during the day to power your home through the evening and overnight. This allows you to avoid buying expensive electricity from the grid during peak hours.
For this purpose, your battery doesn’t need to be massive. You’re looking to cover your “baseload”—the consistent energy draw from appliances like your fridge, router, and devices on standby—plus your typical evening usage from cooking, lighting, and entertainment. A home energy storage system that matches your average overnight consumption is usually sufficient.
Provide Backup Power During Outages
Sizing a battery storage system to navigate a power cut involves assessing your energy needs and the duration of the outage you want to prepare for. Start by calculating your critical power requirements—list the essential appliances and devices you need to keep running (e.g., lights, refrigerator, medical equipment) and their wattage. Multiply their combined wattage by the number of hours you expect the power cut to last to determine the total energy capacity required, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Factor in inefficiencies, as batteries typically lose some energy during charging and discharging and consider adding a buffer for unexpected needs. Additionally, evaluate the battery’s discharge rate to ensure it can handle peak power demands. For longer outages, pairing the battery with a renewable energy source like solar panels can help recharge it and extend its usability.
Whole home back up and emergency power supply system’s come at an additional cost to your home energy storage system, so if you aren’t affected greatly by power cuts you might not need to install this element. However, with energy security becoming an ever-increasing cause for concern it could prove a beneficial investment to future proof your property and get the most out of your battery storage system.
If you require whole home back-up it is likely you will require a Gateway to transfer the home temporarily off grid allowing your battery storage system to support the home until power is restored. Manufacturers such as Tesla, Sigenergy, Enphase and Hanchu provide gateway or controllers which undertake this function.
Emergency power supplies differ in that they target critical loads such as sockets to provide a limited amount of power during power outages.
Whole-Home Backup System via Gateway
- Purpose: Provides seamless power to the entire home during an outage, using a home battery storage system.
- Scope: Powers all circuits in the home, including high-energy appliances like air conditioning, heating, and electric ovens.
- Setup: Utilizes a gateway (a smart energy management device) that integrates with the home battery system. The gateway automatically detects outages and switches the home to battery power.
- Advantages:
- Whole-home coverage ensures no part of the house is left without power.
- The gateway can intelligently manage energy usage, prioritizing critical loads if the battery capacity is limited.
- Often works in tandem with solar panels, allowing the system to recharge during daylight hours for extended backup.
Emergency Power Supply
- Purpose: Provides power to a limited number of essential circuits during a power outage.
- Scope: Typically powers only critical appliances or systems, such as lights, refrigerators, medical devices, or a few outlets.
- Setup: Often involves a manual or automatic transfer switch that connects specific circuits to the backup power source (like a generator or battery).
- Limitations:
- Does not power the entire home.
- Requires careful planning to determine which circuits are prioritized.
- May not support high-energy appliances like HVAC systems or electric water heaters.
Achieve Near Energy Independence
For those aiming to minimise their reliance on the grid as much as possible, a larger system is required. This means storing enough energy to cover almost all your needs, including running high-demand appliances like heat pumps, immersion heaters, and even charging an electric vehicle (EV).
This approach requires a battery capacity that can meet your entire average daily consumption, with a buffer for cloudy days. These systems often involve stacking multiple battery modules to achieve the desired capacity.
Buying and Storing Cheaper Energy
When paired with time-of-use (TOU) tariffs, home energy storage systems offer a smart and cost-effective way to manage energy consumption. TOU tariffs charge different rates for electricity depending on the time of day, with lower rates during off-peak hours and higher rates during peak demand periods. By using a home energy storage system, homeowners can store energy purchased at lower off-peak rates and use it during peak hours when electricity prices are higher. This approach not only reduces electricity bills but also enhances energy independence and efficiency. The potential savings and usage patterns directly influence the sizing of the battery, as a larger capacity may be required to store enough energy to cover peak periods or multiple high-rate intervals. Properly sizing the battery ensures it aligns with your household’s energy consumption patterns and the TOU tariff structure, maximising financial benefits while minimising upfront investment.
Step 3: Account for High-Demand Appliances
Standard household appliances don’t use much power individually, but some items can drain a battery very quickly. It’s vital to factor these into your calculations.
- Electric Showers & Immersion Heaters: These devices have a very high power rating (often 7-10 kW). While they only run for short periods, they can overload a smaller battery’s inverter. Ensure your home energy system’s peak output can handle these appliances.
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging: This is the single biggest energy consumer for many modern households. A typical 7kW home charger will draw 7 kWh for every hour it’s active. If you plan to charge your EV from your home energy storage, you will need a significantly larger system. For example, adding 20 miles of range could use 5-7 kWh, which would deplete an average-sized battery.
- Heat Pumps: Air and ground source heat pumps are efficient, but they have a constant energy draw during colder months. A heat pump can use between 10 to 25 kWh per day, meaning your battery needs to be sized to accommodate this sustained load.
Step 4: Putting It All Together – Sizing Recommendations
Choosing the right battery size isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. It comes down to your daily electricity use, the appliances you need to power, and your ultimate energy goals. Are you looking for a safety net for occasional outages, or do you want to run your entire home on stored energy?
Now let’s translate this into real numbers. Based on household size and energy goals, here are some typical recommendations for UK homes:
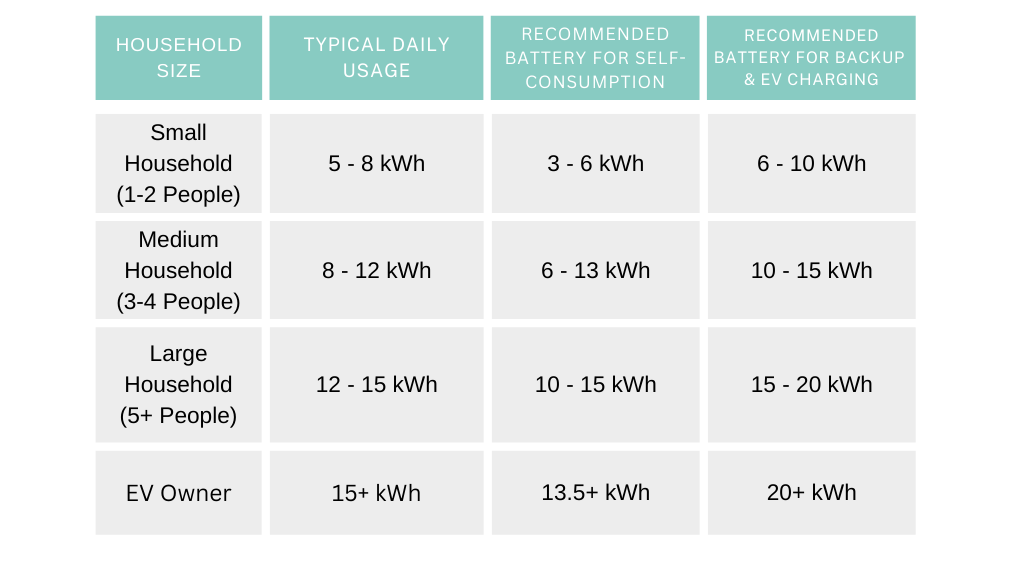
Many modern battery systems are modular. This means you can start with a smaller capacity (e.g., 5 kWh) and add more modules later as your energy needs grow or your budget allows.
- Small Household (1–2 people): A 5–10 kWh battery is a great fit for providing overnight power and backing up key appliances.
- Medium Household (3–4 people): A 10–20 kWh system will cover your evening energy needs and offer substantial backup power.
- Large Household (5+ people)and EV owners: Systems of 20 kWh or more are required for large households or EV Owners. Stacking multiple batteries is a common strategy to meet high demand.
Do You Even Need a Battery? When to Say No
While home energy storage has fantastic benefits, it isn’t the right move for every homeowner. You might be better off without a battery if:
Comparing the Top Home Energy Storage Brands
Choosing a home energy storage system is a major decision that balances your goals, budget, and lifestyle. By understanding your daily energy use and exploring the top brands, you can unlock energy independence and secure a reliable power source for years to come.
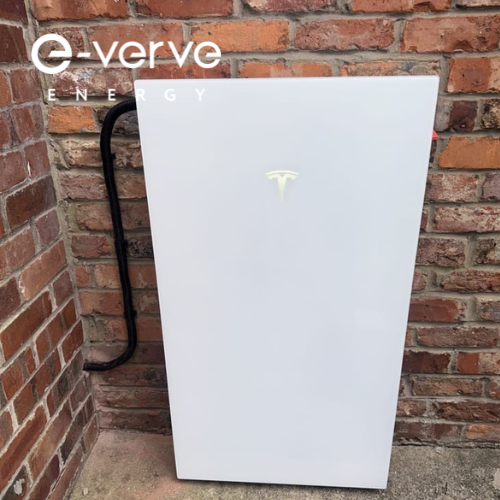
Tesla Powerwall 3
- Capacity: 13.5 kWh per unit
- Dimensions: 1100 mm x 609 mm x 193 mm (43.3 in x 24 in x 7.6 in)
- Key Features: An integrated solar inverter simplifies the system, while seamless backup transition keeps your power on without a flicker. It offers Wi-Fi and app monitoring and is scalable up to 10 units. It comes with a 10-year warranty and a weather-resistant design.
- Pros: High capacity, sleek all-in-one design, trusted brand reliability.
- Cons: Higher price point, locks you into the Tesla ecosystem.
- Best for: Homeowners wanting a premium, integrated system with powerful backup capabilities, especially those with high energy needs or an EV.
- Tesla Datasheet

Sigenergy (SigenStor)
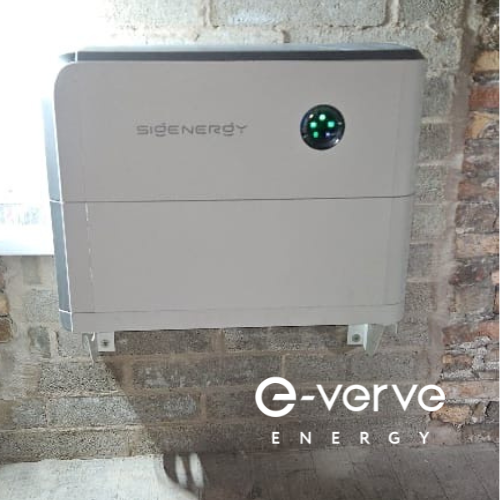

- Capacity: Stackable 5 kWh or 8 kWh modules, expandable up to 48 kWh per stack.
- Dimensions: Per 5 kWh module: 740 mm x 195 mm x 350 mm (29.1 in x 7.7 in x 13.8 in)
- Key Features: A 5-in-1 unified system combining the battery, inverter, EV charger, energy manager, and solar input. It’s IP65 weatherproof and highly modular for future expansion.
- Pros: Extremely flexible and customizable. You can start small and add capacity later. The integrated EV charging is a huge plus.
- Cons: As a newer brand, it has less name recognition than some competitors.
- Best for: Anyone who loves customisation. It’s perfect for starting with a smaller system and expanding as your family or energy needs grow.
- SigenStor Datasheet
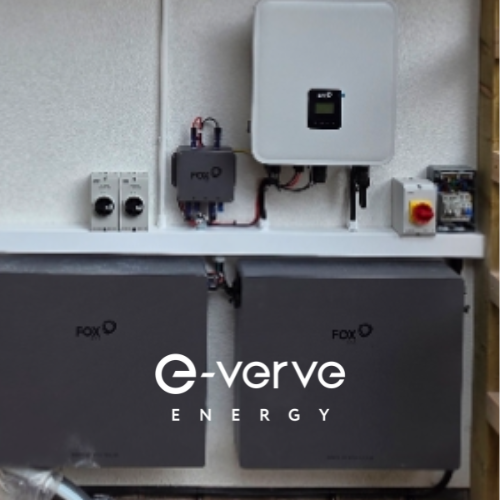
Fox ESS Batteries
- Capacity: Offers a wide range of module sizes, from 2.88 kWh to 28.21 kWh.
- Dimensions: (ECS2900 model) 480 mm x 165 mm x 465 mm (18.9 in x 6.5 in x 18.3 in)
- Key Features: Highly compatible with third-party inverters, making it great for retrofits. It boasts high efficiency and can be mounted on the floor or wall.
- Pros: A very cost-effective and reliable choice. Its flexibility makes it easy to size for existing solar systems.
- Cons: The design is more industrial, and the smart features and app experience may not be as polished as premium brands.
- Best for: Budget-conscious homeowners and those looking to add storage to an existing solar setup without replacing other components.
- FOX ESS Datasheet

Fogstar Batteries

- Capacity: Various options available, including a popular 5.12 kWh rack-mounted unit that is easily scalable.
- Dimensions: (51.2V/100Ah rack) 483 mm x 500 mm x 177 mm (19 in x 19.7 in x 7 in)
- Key Features: Uses safe and long-lasting Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) chemistry. Known for its advanced Battery Management System (BMS), technical transparency, and extremely long cycle life (up to 6,000 cycles).
- Pros: Excellent safety profile and longevity. Highly scalable and customisable, with strong after-sales support.
- Cons: May require more technical planning to install, making it a favorite of advanced users and DIY enthusiasts.
- Best for: Users prioritising long-term value, safety, and customisation, especially for off-grid homes.
- Fogstar Battery Ranges
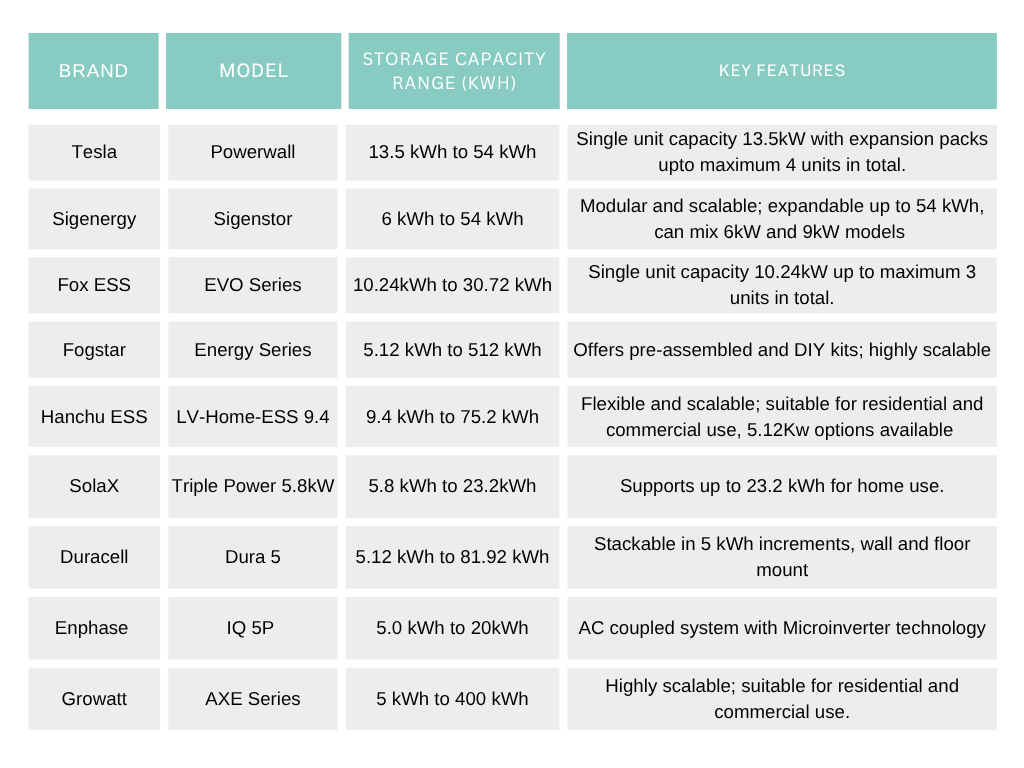
How do the above models compare to the rest of the market? For a wider brand comparison we’ve put together the table below with the key features of each model
Pairing Your Battery with Your Solar System
To get the most out of your investment, your battery and solar array should be properly matched. A good general ratio is to aim for a battery capacity that is 1.5 to 2.5 times your solar system’s kilowatt (kW) rating.
How much battery storage do I need? – Your Next Step!
Answering “How much battery storage do I need?” is a process of self-assessment. Start by analysing your bills, defining your goals, and considering your future needs. With this information in hand, you are ready to have a productive conversation with a professional installer. They can provide a detailed quote and final recommendation to help you make a confident investment in your home energy storage system.
How Can E-Verve Energy Help?
We are officially The Most Trusted Solar Panel Installers of 2024 and with over 10 years in the Industry your in safe hands! We are fully OZEV and MCS accredited, TrustMark approved and proud members of both RECC and CPA. This means that all projects are fully protected and completed by our accredited tradesmen
So now that you understand the key factors and how to calculate your energy needs, take the next step by using our interactive quote tool!
Get your home energy storage cost upfront with no pressure to commit and see how much battery storage could save on your bills! We’re here to help you find the perfect setup for your home.
Get Your Custom Solar Quote in Minutes
Select your setup and receive your tailored solar quote instantly.
120+ Google Reviews
Have more questions?
That’s okay, we’ve answered some of the more commonly asked questions here but if you still have questions, just get in touch and we’ll be happy to provide any support you need.

