How Long Do Solar Batteries Last?
How Long Do Solar Panel Batteries Last in the Real World?
Most solar batteries have a lifespan of 10 to 12 years, so you can expect to need at least two batteries during the 25-year lifespan of a typical solar panel system.
Lithium-ion batteries are currently the most common and widely used battery storage option in the UK, renowned for their reliability and efficiency. Although the exact lifespan of a solar battery varies depending on the type and how it’s used, most reputable manufacturers provide a 10-year warranty on their products, ensuring peace of mind with your investment.
If you want your solar panel batteries to last as long as possible, regular maintenance and active monitoring are essential—simple habits that can stretch out the usable life of your battery and keep it performing efficiently. Taking these steps also helps you maximise your return on investment, as a properly maintained battery delivers more value over its life.
Understanding how long do solar batteries last and the factors that affect their longevity will help you plan ahead and make the most informed choice possible. In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about how long solar panel batteries last and how to maximise their performance in your home.
Types of Solar Batteries
As solar battery technology has advanced, homeowners now have several storage options to fit different needs, budgets, and ambitions. Understanding the main differences between battery types is essential for making an informed choice and ensuring your system delivers maximum benefit.
The top contenders in the solar battery market include lithium-ion, sodium-ion, and newer technology such as vanadium flow batteries. Each type brings its own features, performance capabilities, and best-fit scenarios. Whether you’re looking for high efficiency in a compact space, a budget-friendly backup, or a large-scale solution for long-duration storage, there’s a solar battery designed for your needs. This guide will explore these key technologies to help you find the perfect match for your energy goals
Lithium-Ion
This is the most common type of battery for home energy storage today. Known for their high energy density and efficiency, they pack a lot of power into a compact size.
- Pros: High efficiency, deep depth of discharge (DoD), and a relatively long lifespan.
- Cons: Higher initial cost compared to other types.
- Average Lifespan: 10 to 15 years.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4 or LFP)
A subtype of lithium-ion, LFP batteries are gaining popularity for their enhanced safety and stability. They are less prone to overheating than other lithium chemistries.
- Pros: Excellent thermal stability, long cycle life, and non-toxic materials.
- Cons: Slightly lower energy density than other lithium-ion types, which can make them bulkier.
- Average Lifespan: 10 to 15 years.
Lead-Acid
Lead-acid batteries are a tried-and-true technology that has been used for decades. They are often the most affordable option upfront.
- Pros: Low cost and reliable technology.
- Cons: Shorter lifespan, lower depth of discharge (meaning you can’t use as much of the stored energy), and require regular maintenance. They are also heavy and bulky.
- Average Lifespan: 5 to 7 years.
Vanadium Flow Batteries
These are a newer, more advanced type of battery. They use a liquid vanadium electrolyte to store energy, which offers some unique advantages for large-scale energy storage projects.
- Pros: Extremely long lifespan (can last for decades with minimal degradation), 100% depth of discharge, and easily scalable.
- Cons: High initial cost and lower energy density, requiring more space. They are still less common for residential use.
- Average Lifespan: 20+ years.
Sodium Batteries
Sodium-ion batteries are an emerging technology that offers a promising alternative to lithium-ion, primarily because sodium is an abundant non toxic material which is extracted from sea water as a by product of the desalination process. This makes sodium a real contender for the next generation of battery storage products.
- Pros: Made from cheap, sustainable materials, they perform well in a wide range of temperatures due to the sodium’s lower ionic resistance in the battery cells which provides consistent power outputs .
- Sodium batteries are easier to dispose of at their end of usable life due to the non-toxic nature, making parts or the cells of Sodium Batteries recyclable is another element which manufacturers may look to implement to make even more sustainable.
- Cons: Newer technology with fewer manufacturers and a lower energy density than lithium-ion.
- Average Lifespan: 10 to 15 years.
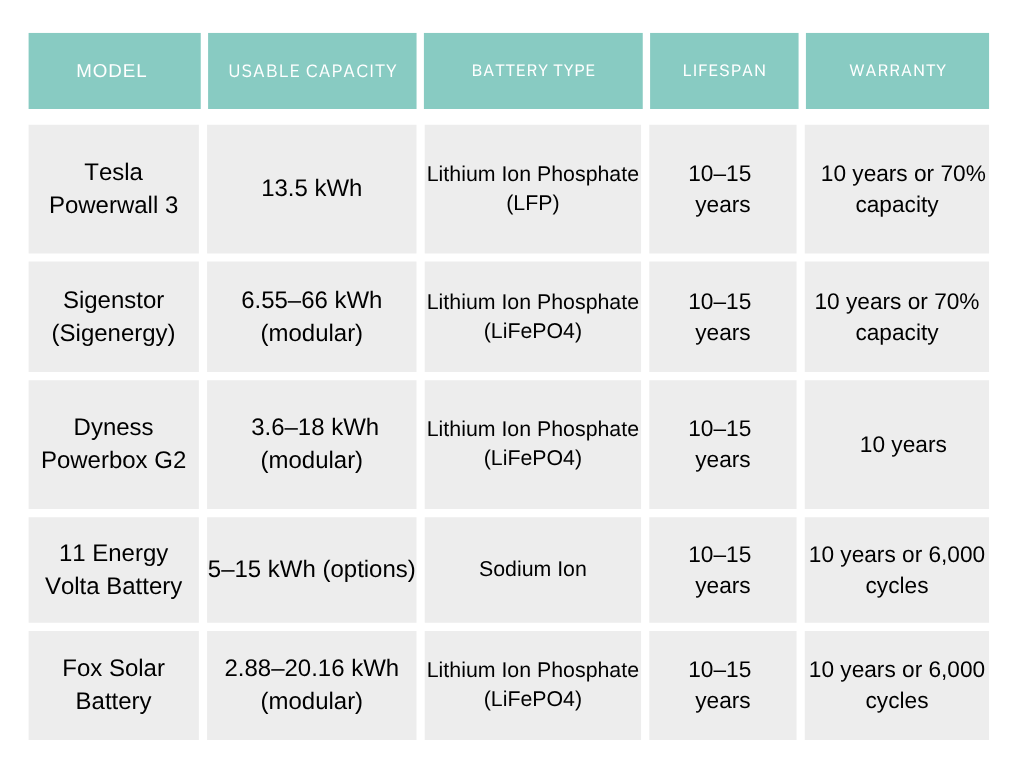
Manufacturer and Product Examples
Several leading manufacturers offer high-quality solar batteries. Here are a few popular options:
Tesla: Powerwall 3
The Tesla Powerwall 3 is a cutting-edge energy storage solution designed to integrate seamlessly with solar panel systems.
Tesla primarily use an air cooling management system circulating natural air around the system to ensure the battery system operates effectively. Mechanical fans with low noise output activate when the battery cell temperatures increase to control heating.
Tesla battery management system (BMS) actively manages the performance of the battery using in-built data driven algorithms.


Sigenergy: Sigenstor
SigenStor batteries are compatible with both single and three-phase systems which offers versatility as batteries of different capacities can be stored in the same modular stack.
The SigenStor battery storage system manages performance using a combination of AI and temperature sensors to maintain battery health and optimise system performance.
SigenStors weather compensation feature predicts battery use based on historical energy use data and upcoming forecasts to proactively manage battery charge and discharge.
Dyness: Powerbox G2
Dyness solar batteries are recognised for their modular design, allowing users to scale their energy storage capacity based on their specific needs. These batteries are ideal for both residential and commercial applications, offering flexibility and efficiency.
Dyness batteries come with a battery management system which controls energy use and manages temperature change and heating


11 Energy: Volta Battery
11 Energy’s sodium-ion Solar batteries offer an alternative to the more common Lithium-ion products.
Battery management systems (BMS) control the system in a similar way to Lithium-Ion products although the level of heating and temperature control reduces due to the thermal stability of the sodium-ion cells.
FOX ESS: Solar Battery
Fox solar batteries are celebrated for their high efficiency and advanced technology. These systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with solar panel installations, providing a dependable energy storage solution.
The newer range of Fox EP batteries now have heating in-built heating controls to maintain cell temperatures and battery performance.

To maximise longevity of your battery storage system ensure your batteries are installed in a suitable location to align with the build specification and manufacturers recommendations. Operating the batteries at a consistent rate also helps to maintain a healthy battery. If you are charging batteries overnight via an off-peak tariff consider spreading the charge across the whole off peak window duration (5-6 hours) as opposed to charging to full capacity in less time.
Factors Influencing Solar Battery Lifespan
Several key factors determine how long your solar battery will perform optimally.
- Battery Type: As discussed, LFP and flow batteries generally last longer than lead-acid or standard lithium-ion batteries.
- Depth of Discharge (DoD): DoD refers to the percentage of the battery’s total capacity that is used. Regularly draining a battery to 100% will wear it out faster. Most manufacturers specify a recommended DoD (often 80-90%) to maximize lifespan.
- Temperature: Batteries are sensitive to extreme heat and cold. High temperatures accelerate chemical degradation, while extreme cold can reduce performance. Installing a battery in a temperature-controlled environment is ideal.
- Charge and Discharge Rates: Charging or discharging a battery too quickly can stress its components and shorten its life. A slower, more consistent rate is healthier for the battery.
- Cycling and Age: A “cycle” is one full charge and discharge. Every battery is rated for a certain number of cycles. Over time, all batteries degrade naturally, a process known as calendar aging.
- Installation and Maintenance: Proper installation by a certified professional is crucial. While many modern batteries are low-maintenance, regular check-ups and following manufacturer guidelines are important.
Signs Your Solar Battery May Need Replacement
Even the best batteries eventually wear out. Watch for these signs that it might be time for a replacement.
- Decreased Storage Capacity: The most obvious sign is that your battery doesn’t hold as much charge as it used to. If you find it can no longer power your home through the night, its capacity has likely diminished.
- Reduced Performance: You might notice the battery struggles to power high-demand appliances or that it takes much longer to charge.
- Increased Maintenance: For batteries like lead-acid, a sudden need for more frequent maintenance (like adding distilled water) can indicate a problem.
- Outdated Technology: If your battery is over a decade old, newer models will likely offer better efficiency, capacity, and features. Upgrading could provide better performance and a greater return on investment.
How to Maximise Your Solar Battery’s Lifespan
You can take several steps to get the most out of your battery investment.
- Install in a Cool, Dry Place: Protect your battery from direct sunlight and moisture. A garage, utility room, or basement is often the best location.
- Use the Recommended Depth of Discharge (DoD): Avoid completely draining your battery. Set your system to maintain a minimum charge level as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Regularly Maintain and Monitor: Use the battery’s monitoring software or app to keep an eye on its performance. Check for any error messages or unusual behavior and schedule professional maintenance as needed.
Understanding Solar Battery Cycles
The way you cycle your battery has a direct impact on its health and overall lifespan.
A battery’s lifespan is most accurately measured in cycles—one cycle being a complete charge and discharge. The best solar batteries available on the market typically offer between 6,000 and 10,000 cycles. For most households, the battery will go through one to two cycles per day. If you’re participating in a scheme like the Smart Export Guarantee and exporting your excess electricity, two cycles per day is even more common.
Sticking to one or two cycles daily helps balance performance and longevity. Too few cycles can cause some battery chemistries to degrade in a “use-it-or-lose-it” scenario, while too many cycles will wear out your battery and shorten its usable life. Be sure your battery is rated for your intended use—especially if you plan to make the most of energy export programs.
Make the Right Choice for Your Home: How Long Do Solar Batteries Last?
Choosing the perfect solar panel battery is a crucial step toward maximising your solar investment and achieving reliable home energy storage. When considering how long solar batteries last, it’s important to weigh the factors discussed—from battery technology and lifespan to cycles and manufacturer warranties. With proper maintenance and an informed selection, you can expect a typical solar battery to last 10–12 years, and you may need at least two batteries over the lifetime of your solar panels.
Trust E-Verve Energy for Expert Guidance and Quality Solar Battery Options
At E-Verve Energy, we specialise in helping homeowners find the best solar battery solutions tailored to their needs. Our team offers expert advice on the latest lithium-ion, LiFePO4, flow, and other battery types, ensuring you understand how long your solar panel batteries can last and which options will deliver performance, reliability, and long-term savings.
We take the guesswork out of choosing the right solar battery by:
- Assessing your current and future energy requirements
- Providing detailed comparisons of leading products and models
- Explaining warranties, maintenance needs, and optimal system configurations
- Offering professional installation and ongoing support for maximum battery lifespan
Whether you want to upgrade your existing solar panel setup or are installing your first energy storage system, E-Verve Energy is your trusted partner for making smart, future-proof choices.
Reach out to E-Verve Energy- The Most Trusted Renewable Energy Installer of 2024! today to discover how we can help you get the most out of your solar batteries!

Get Your Custom Solar Quote Today
Select your ideal setup and receive a tailored quote in minutes.
120+ Google Reviews
Have more questions?
That’s okay, we’ve answered some of the more commonly asked questions here but if you still have questions, just get in touch and we’ll be happy to provide any support you need.

